What is Decentralized Storage?
What is decentralization?
Decentralized networks have a lot of advantages. Click here to learn more!Data transmitted over the internet is often processed and stored in large-scale servers. These centralized servers are controlled by internet service providers and web services like Google and Amazon. This is known as the client-server model and it is the backbone of our world wide web. It is the most efficient way to send information back and forth between users. Data is sent from one user, funneled through a centralized server, and then sent to its intended recipient; the centralized server does most of the processing and is the key facilitator in this transfer.
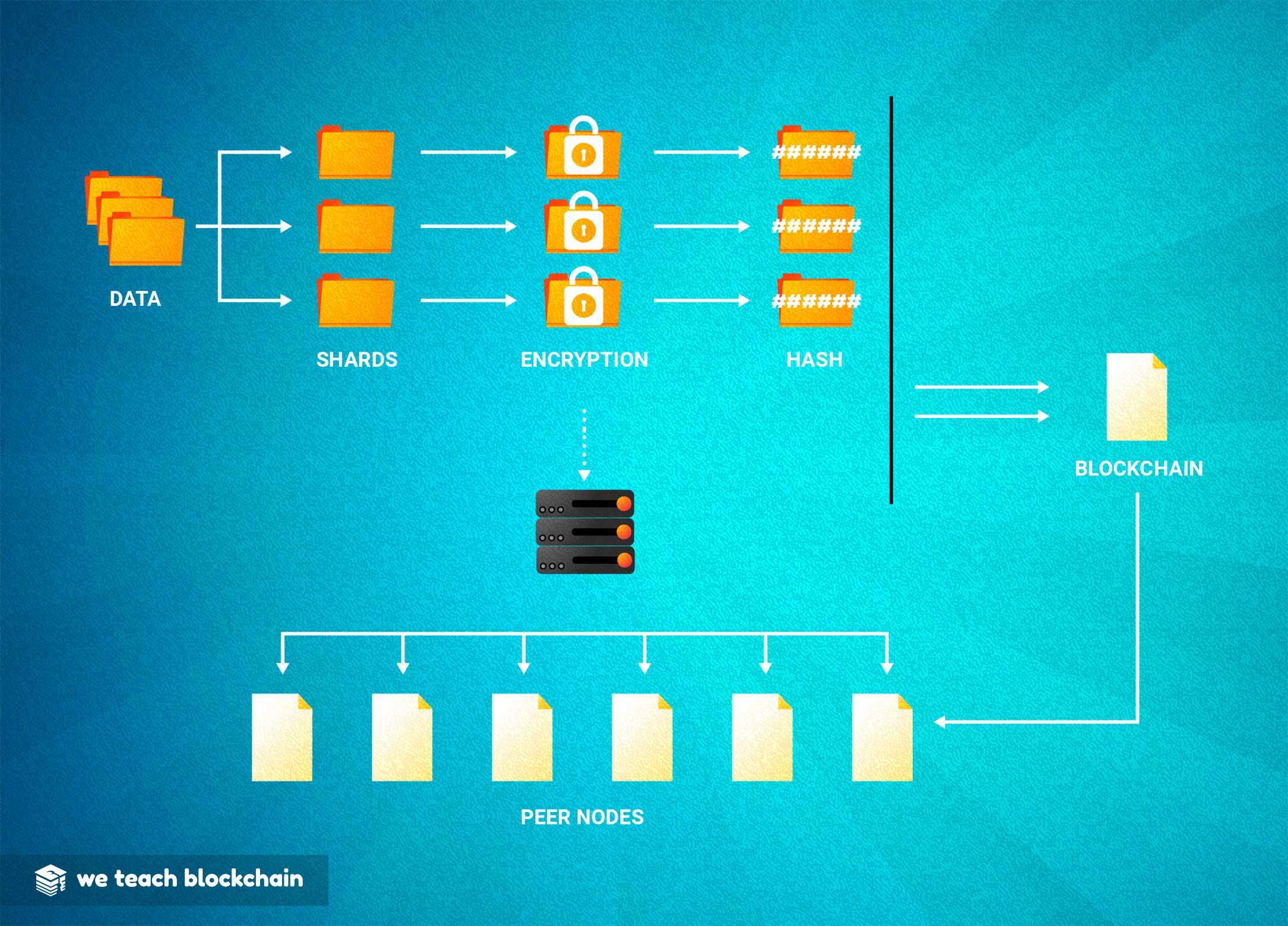
HOW DECENTRALIZED STORAGE WORKS
Decentralized storage is only possible because a large number of computers share the load. In order to store a file on the decentralized web, it is broken into many very small pieces, each of which has a unique signature associated with it. These are then distributed to the members of the network!However, there are significant issues with storing large amount of data in these centralized servers. There have been many recent hacks and other data breaches of businesses and organizations that have custody of our personal information. This potential for data loss puts customers at risk of their personal information being compromised. Since all customer data is stored in one place, it is an easy target for hackers, as illustrated by the Equifax and Facebook hacks.
Blockchain technology offers an alternative way for information to be stored, known as peer-to-peer storage. Instead of a centralized, vulnerable server, information is duplicated and stored by every single user of the network. When information is downloaded by a user, pieces of the desired file are gathered from several users’ storage. While there can be efficiency drawbacks to this structure, it is much more secure, and as more members begin to use these standards, efficiency will increase as well!
Check out our IPFS Demo or our free Decentralized Storage Course.