Cryptocurrencies are secured by cryptography. Having a basic understanding of asymmetric cryptography is a prerequisite for comprehending how cryptocurrencies work.
Asymmetric or public/private key cryptography was developed in the 1970s. Prior to then, the only cryptography available was symmetric. Let’s take a look at how symmetric cryptography works to gain some insight into why asymmetric cryptography was developed and the advantages it has.
Alice and Bob want to communicate securely with one another.

To do this Alice creates a message to Bob and scrambles it using a specific formula also called an encryption algorithm. This is done using a secret, or a key.
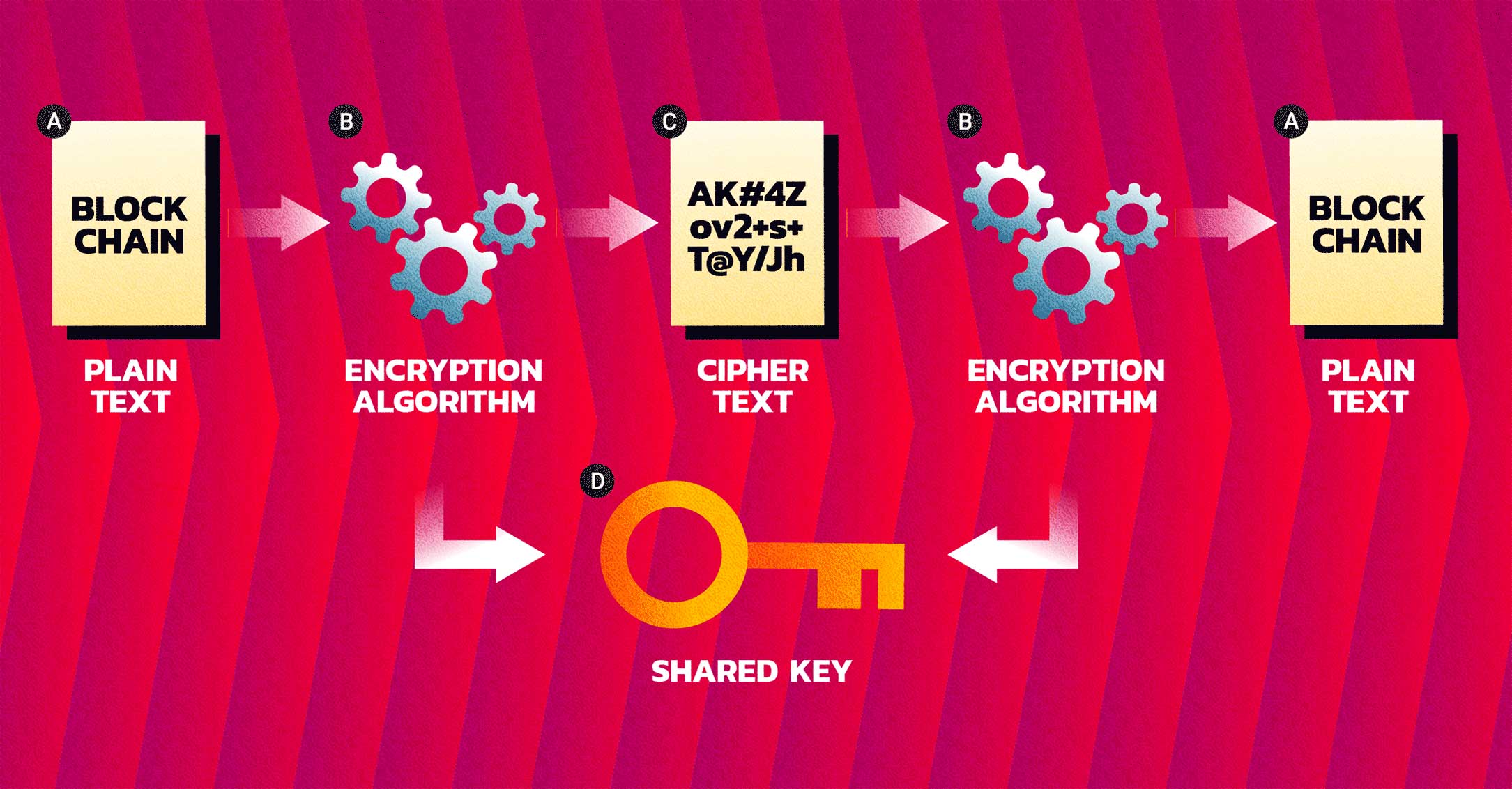
Encryption Process
A: Plain text; B: Encryption Algorithm; C: Cypher text; D: Shared Key.Let’s look at a much more simplified example of this…
Alice wants to encrypt the word “Hello” to send to Bob. She uses the very simple formula of taking each letter in the word and changing it to the letter two spaces over in the alphabet. This formula is the algorithm or key.
Simple Cypher Encryption
Hello → [ move over two spaces in the alphabet ] → KgnnqSimple Cypher Decryption
Kgnnq → Key → HelloIf Bob knows this formula, then Alice can securely transmit this message to Bob, and it will look like gibberish to anyone who intercepts the message.
This works just fine; the problem is with transmitting the key to Bob. How do you securely transfer the key? Anyone who intercepts it will be able to read all the communication between Alice and Bob.
A real world analogy for asymmetric encryption would be a locked mailbox. Your address is your public key, while the key that unlocked the mailbox is analgous to your private key. Anybody can come along and drop you a letter if they know your address, but only you can retrieve the messages in the mailbox. Anyone can use your private key to send you messges or funds, but they can’t access the rest of your cryptocurrency unless they have your private key.
This is a fundamental weakness in symmetric cryptography that was solved by asymmetric cryptography. Lets see how it’s done in the next lesson!




